AIRSAR
Airborne SAR (AIRSAR) was a prototype JPL earth-observation project equipped with synthetic aperture radar (SAR) — an all-weather imaging tool able to penetrate clouds and collect data at night. Two of the AIRSAR imaging modes used could penetrate into the forest canopy, dry snow cover, and, in extremely dry areas, sand.
AIRSAR was a NASA radar technology testbed to demonstrate new radar technology and acquire data for developing radar processing techniques and applications.
The data are open and freely available to download.
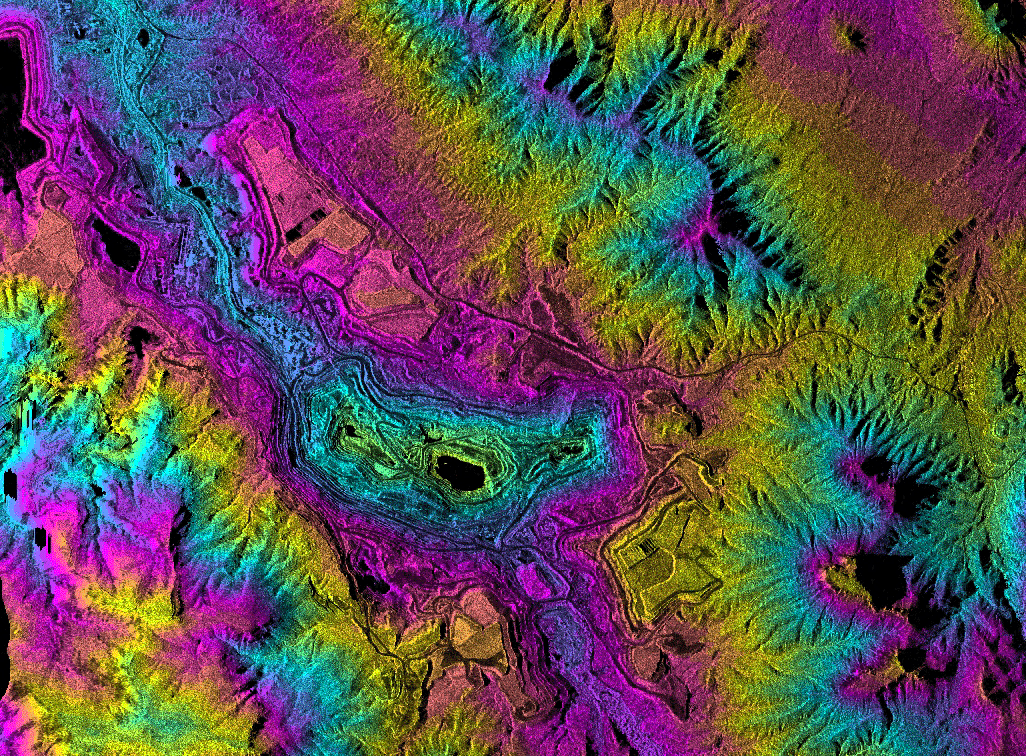
Image: Topographic radar data over the Ray Mine in central Arizona. Colors show elevation information from the mine pits in the center of the image up through the surrounding mountains. These data are being used for mine site and watershed characterization associated with environmental assessment of the area. Image by NASA /JPL


| Dataset Property | P-Band | L-Band | C-Band |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal Coverage | 1988-2004 | 1988-2004 | 1988-2004 |
| Spatial Coverage | Worldwide mission-specific sites | Worldwide mission-specific sites | Worldwide mission-specific sites |
| Frequency/Wavelength | 0.45 GHz/67 cm | 1.26 GHz/23 cm | 5.31 GHz/5.7 cm |
| Polarization | Full | Full | Full |
| Range Resolution | 7.5 m | 3.75 m | 1.875 m |
| Swath Width | 10 km | 10 km | 10 km |
| Off-Nadir Angle | 20-60° | 20-60° | 20-60° |
| File Format | AIRSAR (proprietary), JPG | AIRSAR (proprietary), JPG | AIRSAR (proprietary), JPG |
| Download Information | Data Discovery | Data Discovery | Data Discovery |
| Date Published | 1988-2004 | 1988-2004 | 1988-2004 |
Expand the sections below to view content. Access the full content on a single page by clicking the button.
AIRSAR Technical Specs
| Dataset Property | P-Band | L-Band | C-Band |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal Coverage | 1988-2004 | 1988-2004 | 1988-2004 |
| Spatial Coverage | Worldwide mission-specific sites | Worldwide mission-specific sites | Worldwide mission-specific sites |
| Frequency/Wavelength | 0.45 GHz/67 cm | 1.26 GHz/23 cm | 5.31 GHz/5.7 cm |
| Polarization | Full | Full | Full |
| Range Resolution | 7.5 m | 3.75 m | 1.875 m |
| Swath Width | 10 km | 10 km | 10 km |
| Off-Nadir Angle | 20-60° | 20-60° | 20-60° |
| File Format | AIRSAR (proprietary), JPG | AIRSAR (proprietary), JPG | AIRSAR (proprietary), JPG |
| Download Information | Data Discovery | Data Discovery | Data Discovery |
| Date Published | 1988-2004 | 1988-2004 | 1988-2004 |
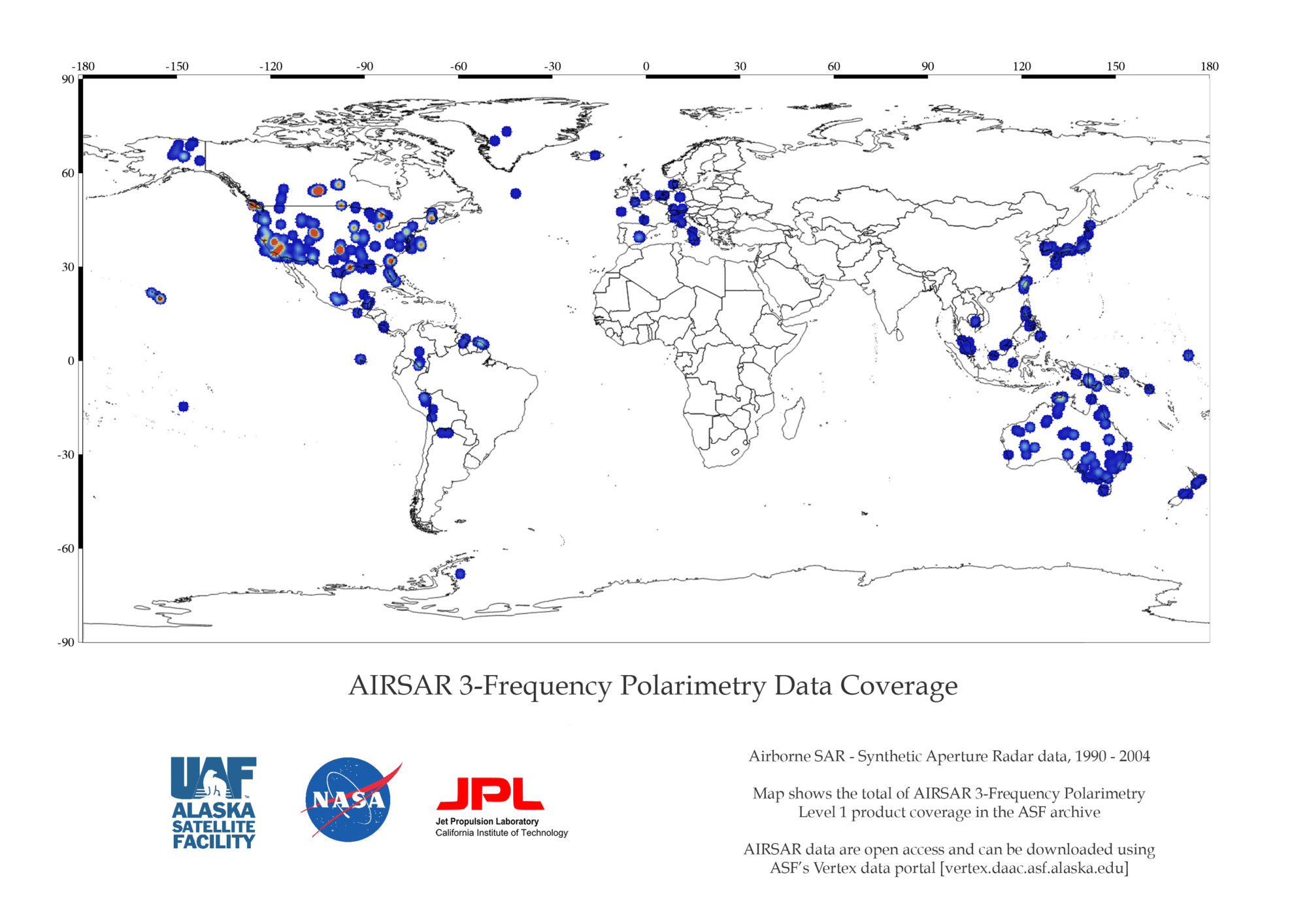
AIRSAR 3FP Coverage Map
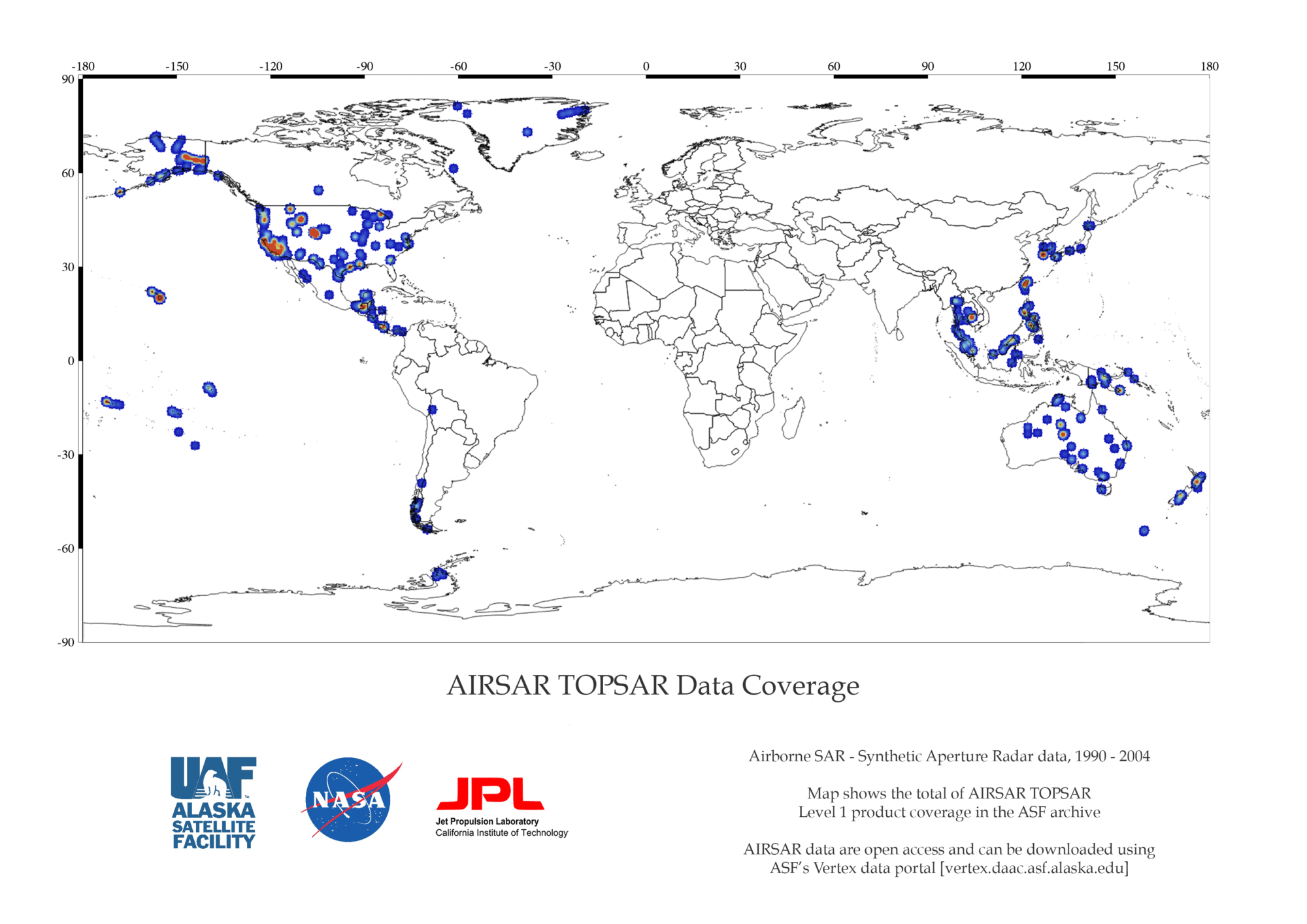
AIRSAR DEM Coverage Map
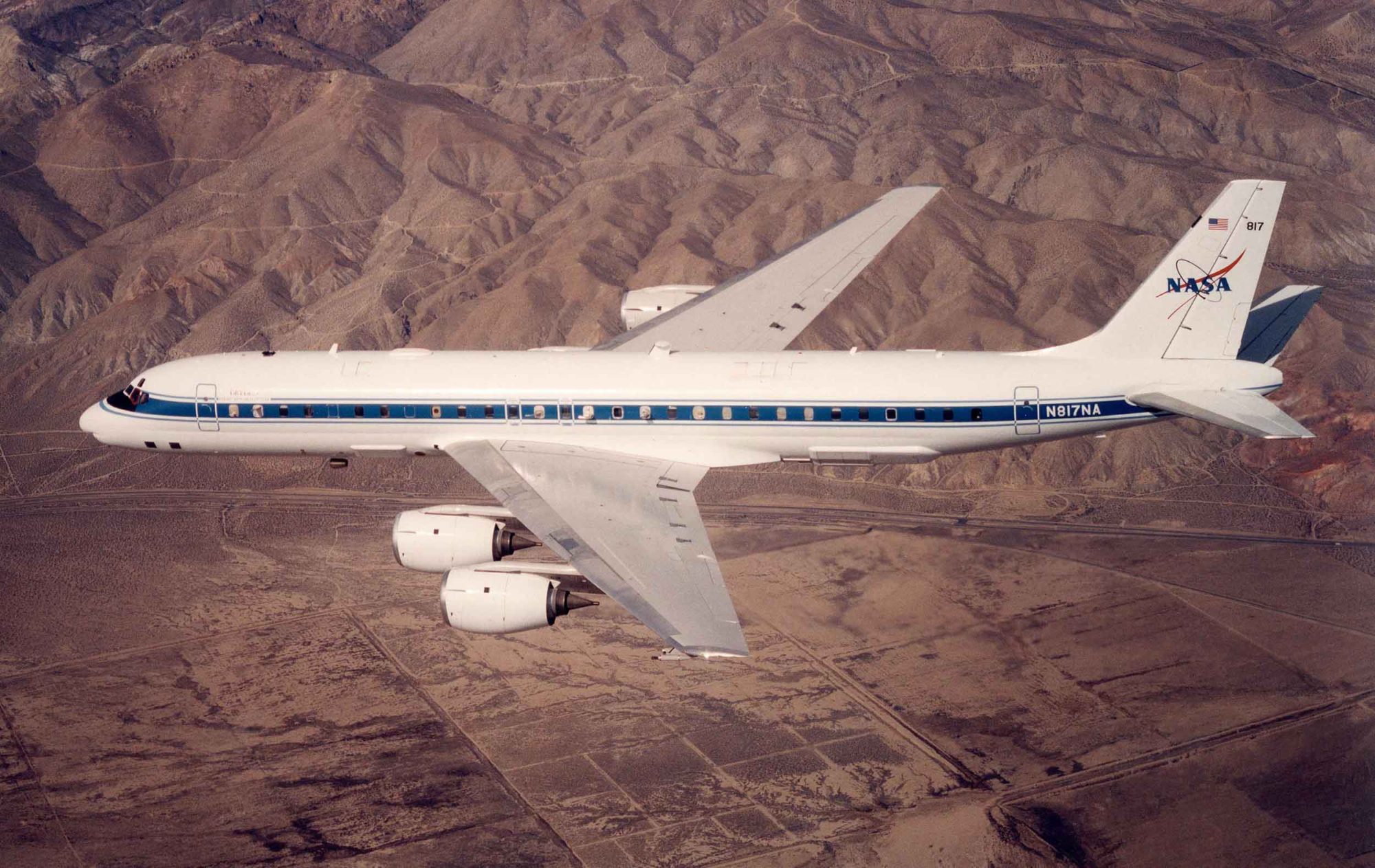


The AIRSAR instrument (panels behind wing) are mounted aboard a modified NASA DC-8 aircraft. During data collection, the plane flies at 8 kilometers over the average terrain height at a velocity of 215 meters per second.
The AIRSAR radar antennas are mounted on the back part of the DC-8 aircraft. These antennas are used to collect data in all three modes. L-band ATI uses an additional antenna (not shown) located in front of the wings.
See the Product Information tab for details.
| Dataset | DOI |
|---|---|
| AirSAR_TOPSAR | 10.5067/F1SC87EFGT9U |
AIRSAR Products
Dataset Description:
- Airborne SAR — synthetic aperture radar
- 1990-2004
- Primarily covers the United States; other tropical locations included
- Datasets identified by place name
Downloadable Data:
- PolSAR: 3-frequency polarimetry
- TOPSAR: C-, L-, and P-band Compressed Stokes Matrix, C-band TIFF, DEM
- ATI — Along-track interferometry: Interferograms
More detailed product descriptions are available from the AIRSAR website
Find AIRSAR data. No proposals required.
AIRSAR TOPSAR data formats and files
| Format | Product Name | Product Files | Open-source Tools | Can Be Used For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIRSAR | C-band DEM and Compressed Stokes Matrix | c.corgr, c.demi2, c.vvi2 | MapReady, PolSARpro | Polarimetry |
| AIRSAR | L-band Compressed Stokes Matrix | l.datgr | MapReady, PolSARpro | Polarimetry |
| AIRSAR | P-band Compressed Stokes Matrix | p.datgr | PolSARpro | Polarimetry |
AIRSAR PolSAR – AIRSAR ATI (Experimental) data formats and files
| Format | Product Name | Product Files | Processing Level | Open-source Tools | Can Be Used For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIRSAR | 3-Frequency Polarimetry | c.dat, l.dat, p.dat | Compressed stokes matrix | MapReady, PolSARpro | Polarimetry |
| JPG | Along-Track Interferometry | *intf*, *uwScc*, *az*, *uwWrp*, *uwWcc*, *uwWrp, *par, *ppp | SLC, MLC | N/A | Ocean current velocity measurement |
Citation Information
How to Cite AIRSAR Data and Imagery
| Dataset Product | How to Cite | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| AIRSAR Data | Cite data in publications such as journal papers, articles, presentations, posters, and websites. Please send copies of, or links to, published works citing data, imagery, or tools accessed through ASF to [email protected] with “New Publication” on subject line. | Dataset: AIRSAR, NASA [year of data acquisition]. Retrieved from ASF DAAC [day month year of data access]. | Dataset: AIRSAR, NASA 2003. Retrieved from ASF DAAC 7 June 2015. |
| AIRSAR Data | Include credit with each image shown in publications such as journal papers, articles, presentations, posters, and websites. | NASA [year of data acquisition] | NASA 2003 |
Discover AIRSAR data
Researchers can download AIRSAR data from the NASA-sponsored ASF DAAC.
| Data Discovery Tool | Link |
|---|---|
| ASF Vertex Data Search | Vertex |
| Python Search Module | asf_search |
| ASF Search API | ASF Search API |
| NASA Earthdata Search | Earthdata Search |